

Once the test is finished, the neurologist or technician will remove the needle or needles. The needle electrodes transmit this information to a device called an oscilloscope, which displays electrical signals as waves. The needles detect the electrical activity of muscles at rest and while contracted. This may cause some minor discomfort in some people. The following sections describe what to expect from needle EMG and NCV tests.Ī needle EMG test measures how well the muscles respond to electrical impulses.Ī neurologist or assisting technician will insert one or more thin, sterile needles into the muscle. Remove any jewelry, watches, eyewear, or other metal objects before the procedure.Dress in comfortable, loose-fitting clothes.Avoid applying lotions, creams, or body oils for a few days before the test.Bathe or take a shower the night before or the morning of the test to remove excess oil from the skin.


To prepare for the test, a person should:
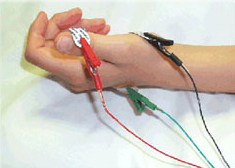
Neurologists and physical medicine and rehabilitation physicians perform EMG tests. numbness, tingling, or paralysis in the limbsĮMG tests also provide information that doctors can use to determine the location and extent of muscle and nerve damage.ĮMG is an outpatient procedure that can take place at a hospital or an office clinic.persistent pain in the feet, legs, arms, or hands.difficulty speaking, chewing, or swallowing.If the motor nerves are damaged or diseased, they can send abnormal electrical signals to the muscles.Ī doctor may order an EMG test if a person has symptoms of a muscle or nerve condition. Motor nerves control skeletal muscle activity, such as walking, speaking, and breathing.ĭamaged or diseased muscle fibers do not function or respond to nerve impulses appropriately. The electrical signals from the nerves trigger muscle contractions. Motor nerve cells, or neurons, transmit electrical signals from the central nervous system to the muscles. Share on Pinterest A person may have an EMG to help diagnose a muscular or neurological condition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
